Cheap oil is good for the economies of the US, Europe and Japan and the recent plunge in prices should support the USD, but for the EUR and JPY the dynamics are more nuanced.
The interpretation many commentators are drawing from plunging oil and commodity prices is that the global economy is slowing and that deflation will become more persistent. However, if the global economy is slowing – cheaper oil will be a good tonic. And low energy prices are actually a form of good deflation for consuming countries.
Nonetheless, for central banks fixated with fears of deflation – the Bank of Japan and European Central Bank – it represents another reason to pursue very expansive monetary policies and even increase them. So in the short to medium term, falling oil prices could be a negative for EUR and JPY. Under normal circumstances lower energy prices would be bullish for both currencies.
By Justin Pugsley, Markets Analyst MahiFX. Follow @MahiFX on twitter
For the US, cheaper energy prices will dampen down inflation and could see the US Federal Reserve hold back on interest rate rises for longer than it anticipated. Indeed, the Fed stuck with its relatively dovish stance, promising to “be patient” at its latest FOMC, but did note that energy is not the only deflationary input.
Cheaper oil = cheaper JPY?
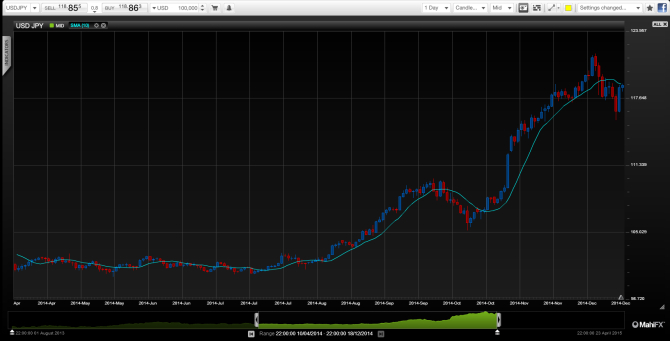
When US rate rises come – they could go up quickly
Rolling back on rate rise expectations will help many of the struggling emerging market currencies, which have become victims of the change in US monetary policy and falling commodity prices.
Meanwhile, US growth is robust and was already expected to accelerate next year. Cheaper energy will further stoke the US economy with the implication that once lower energy prices have fallen out of the inflation numbers – interest rates could rise in H2 and possibly quite quickly.
Interestingly, the USD is increasingly behaving like a ‘risk’ currency as capital flows into assets such as US equities from growth-starved Europe and Japan. This could make the performance of USD more sensitive to numbers such as GDP.
The one big caveat to a rising USD is that if it did trigger a crisis in emerging markets, particularly with countries which borrowed in USD, it could spur central bank action to stem its rise. That’s not on the cards at the moment as Japan, the Eurozone and many others would love a stronger USD so they can more easily export to the more vibrant US in a bid to rediscover growth at home.
